Hypothesis: The intuitive value of online physician ratings has gained acceptance; however, quantifying the online physician rating impact for a hand surgeon remains a challenge. This study evaluated the effect of automated online reviews towards building a referral-based hand surgery practice for both a recent fellowship graduate and established senior hand surgeon.
Methods: This prospective cohort study measured online physician ratings from Yelp and Healthgrades over 28-months for two surgeons in the same practice. Surgeon A, a junior associate starting practice, utilized automated and active online review requests. Surgeon B, a senior, established hand surgeon, utilized passive online review requests. The number of patients who were referred from online review sites was subsequently measured for each surgeon to determine the impact of online reviews based on quantity and value of reviews.
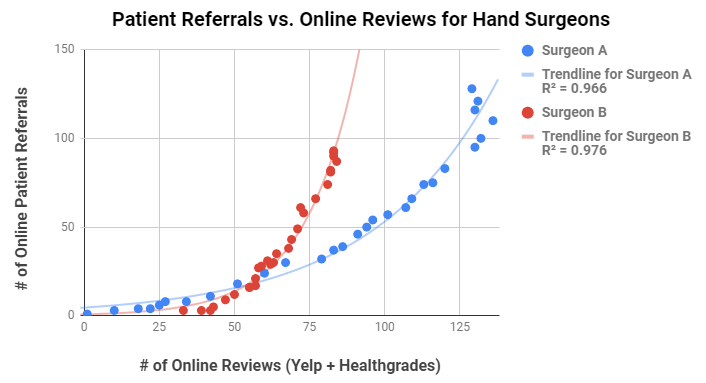
Results: During the study period, Surgeon A increased total reviews from 1 to 129 (net gain of 128) and simultaneously acquired 128 new patients (Figure 1). During the same period, Surgeon B increased total reviews from 33 to 83 (net gain of 50) and acquired 93 new patients from online reviews (Figure 1). Both plots represented exponential practice growth R^2 values of 0.966 and 0.976, respectively.
Summary Points:
– Patient referrals are closely associated with volume of online reviews with R^2 values from 0.96-0.98
– Patient referrals from online reviews are non-linear, resulting in exponential and accelerated practice growth as additional online reviews are acquired
– Online review growth has the potential to augment patient volume for both established and young hand surgeons
© 2025 – SurgiSurvey. All rights reserved.